Buttonwood Poolside Explained Simply

What is Buttonwood?
Buttonwood is a suite of DeFi primitives that facilitate the creation of advanced decentralized financial tools. A key insight of Buttonwood is the idea that all financial structures can essentially be broken down into tranches. The ButtonTranche contracts form the backbone for developing platforms that offer services like debt without liquidation, convertible bonds, options, and even stablecoins independent of fiat.
The Buttonwood Foundation was established based on the principle that the development of future financial systems (DeFi) requires an understanding of historical financial strategies and a foundational approach. While DeFi has incorporated elements like AMMs (Uniswap) and margin lending (Aave), it still lacks many components found in traditional financial systems.

The core contracts of Buttonwood are designed to be permissionless and highly composable, making it straightforward for developers to integrate these by just adding routers and a user interface.
Poolside AMM Explained Simply

Poolside functions as the central liquidity nexus within DeFi for liquid receipt tokens and yield-bearing assets. It is constructed around an innovative automated market maker (AMM) specifically tailored for liquidity providers (LPs) managing tokens such as liquid staking tokens (LSTs) that appreciate in value.
 Poolside introduces a framework that acknowledges the yield generation of tokens, safeguarding this additional value from arbitrage losses. Unlike other AMMs, which subject LPs to potential forfeitures of staking rewards regardless of token or AMM design, Poolside addresses these common pitfalls and stands as the sole decentralized exchange (DEX) capable of supporting sustained, robust markets for LSTs, including Lido’s stETH and BENQI’s sAVAX.
Poolside introduces a framework that acknowledges the yield generation of tokens, safeguarding this additional value from arbitrage losses. Unlike other AMMs, which subject LPs to potential forfeitures of staking rewards regardless of token or AMM design, Poolside addresses these common pitfalls and stands as the sole decentralized exchange (DEX) capable of supporting sustained, robust markets for LSTs, including Lido’s stETH and BENQI’s sAVAX.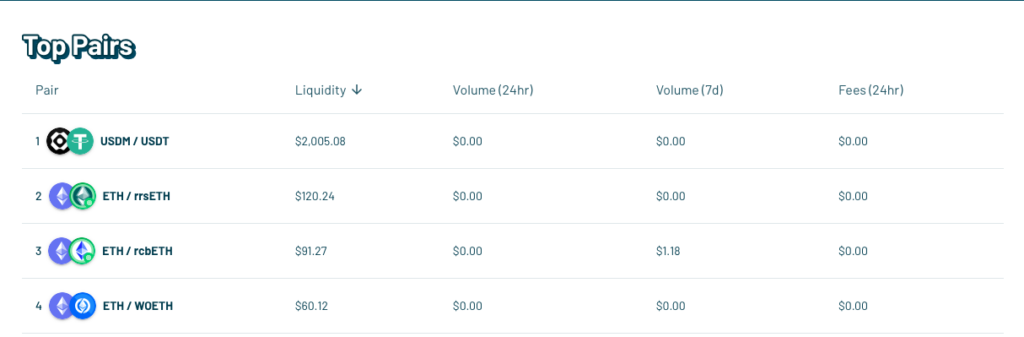
Moreover, Poolside enhances the potential for LPs to maximize earnings through Poolside Party, a non-custodial incentive program that strategically allocates rewards algorithmically. LPs at Poolside can engage their LP tokens in various rewards programs to acquire tokens, on-chain points, NFTs, and more, all while the LP tokens remain in their wallets, fully tradable and operational within broader DeFi. Poolside LPs benefit from trading fees, retain their staking rewards, accrue additional incentives, and can also use their LP tokens as collateral in other DeFi applications.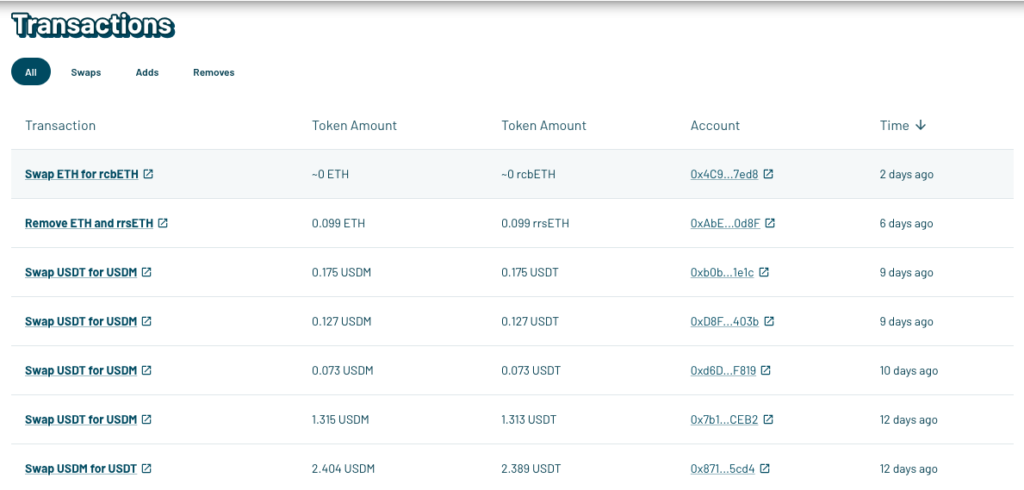 Poolside is essential for the scalability of LSTs and other yield-bearing assets, providing long-term, uninterrupted liquidity within AMMs that supports protocol growth and shields from disruptions due to withdrawals. This stability is vital for liquid staking and lending protocols dependent on sustained collateral to deliver expected returns. The liquidity present in AMMs further enables the use of LSTs as collateral across various DeFi operations.
Poolside is essential for the scalability of LSTs and other yield-bearing assets, providing long-term, uninterrupted liquidity within AMMs that supports protocol growth and shields from disruptions due to withdrawals. This stability is vital for liquid staking and lending protocols dependent on sustained collateral to deliver expected returns. The liquidity present in AMMs further enables the use of LSTs as collateral across various DeFi operations. As the AMM mitigates permanent loss for LPs, Poolside emerges as the most effective venue for incentivizing liquidity for protocols and DAOs. The synergy between protocols and LPs cultivated by Poolside promotes deep markets that support the expansion of LSTs and burgeoning sectors like tokenized real-world assets (RWAs) and yield-bearing stablecoins, forming the bedrock of DeFi.
As the AMM mitigates permanent loss for LPs, Poolside emerges as the most effective venue for incentivizing liquidity for protocols and DAOs. The synergy between protocols and LPs cultivated by Poolside promotes deep markets that support the expansion of LSTs and burgeoning sectors like tokenized real-world assets (RWAs) and yield-bearing stablecoins, forming the bedrock of DeFi.
How to Use Button Swap

The advent of rebasing assets has introduced a series of challenges and opportunities within the decentralized finance (DeFi) sector. A notable challenge was highlighted during the “DeFi summer,” when it became clear that liquidity providers (LPs) faced predictable financial losses during rebasing events. This issue has become particularly critical with prominent rebasing assets like Lido’s stETH.
The AMM Challenge for Liquid Staking Derivatives
The design of Automated Market Makers (AMMs) involves various trade-offs. Until now, most AMM builders have not incorporated adequate measures for Liquid Staking Derivatives in their designs. For instance, Uniswap explicitly warns about the pitfalls for LPs dealing with rebasing tokens. While some developers have attempted alternative solutions, none have thoroughly addressed the core issue: losses for LPs during rebasing and reward-bearing events are both predictable and detrimental.
A Costly Inefficiency
This oversight in AMM design has persisted, representing a significant barrier to enhancing the liquidity of these assets. Current AMMs incorrectly adjust the swap ratio between two assets post-rebase. This mispricing impacts not only rebasing tokens but also reward-bearing assets like Rocketpool’s rETH, where the marginal price is inaccurately altered.
Button Swap, while not addressing every type of impermanent loss, specifically mitigates losses incurred from rewards or token accrual. On Button Swap, tokens from a positive rebase do not enter the active liquidity pools directly. Instead, they are diverted into ‘reservoirs’ that hold inactive liquidity owned by LPs. This design allows the pools to maintain an accurate marginal price between two assets, whether they are rebasing tokens or reward-bearing tokens.
To use Button Swap, connect your web3 wallet.
For this demonstration, we’ll use MetaMask wallet.
Choose the assets you wish to swap and receive. For example here we are swapping ETH for Astrid Restaked cbETH (rcbETH).
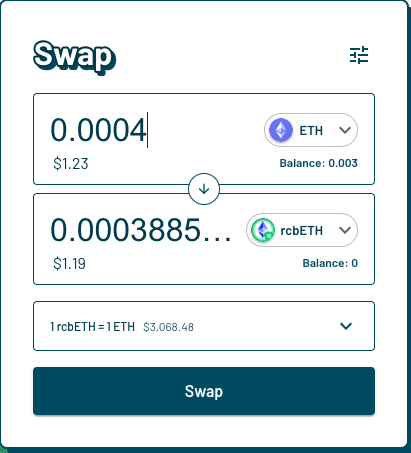
Proceed with your swap.

Sign to give your wallet permission to proceed with the transaction.
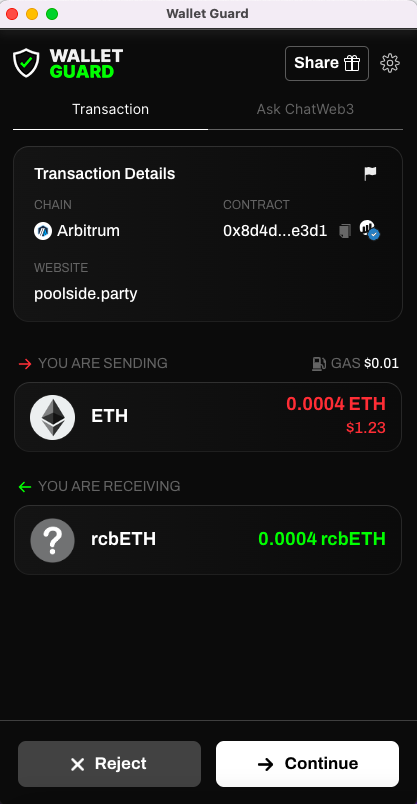
Pay the gas fee.
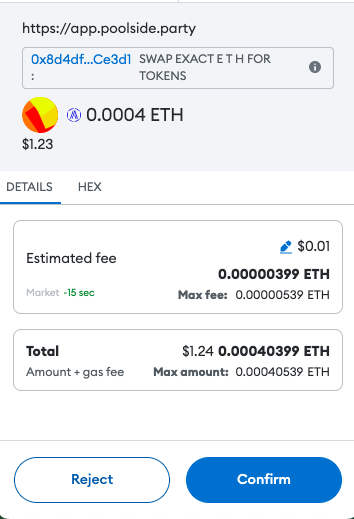 You’ll get confirmation once your transaction has been processed.
You’ll get confirmation once your transaction has been processed. 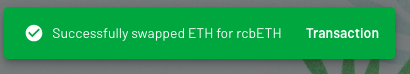
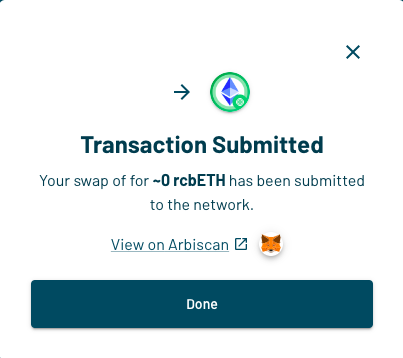 You can also verify the transaction on the block explorer.
You can also verify the transaction on the block explorer. 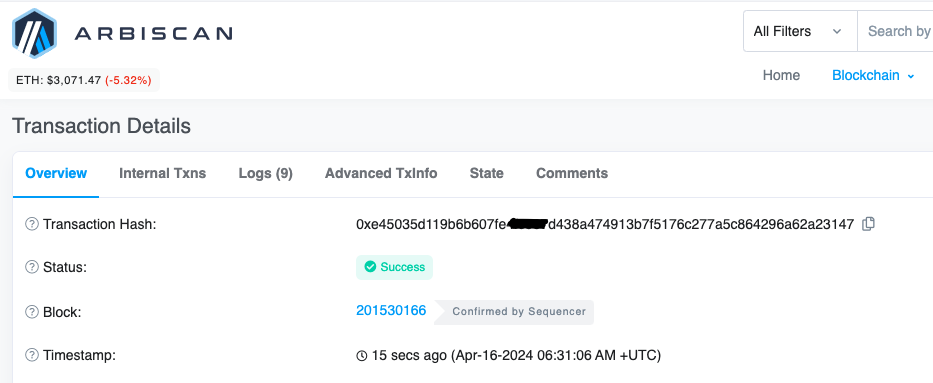
The architecture of Button Swap is particularly suited for the liquid staking market and other areas involving rebasing assets such as Ampleforth, appreciating collateral tokens like Aave’s aTokens or Compound’s cTokens, and reward tokens like ShapeShift’s FOXy. Additionally, Button Swap provides a platform where incentives can act as genuine rewards rather than mere compensations for expected losses.