Top Web3 Digital Assets

What is Web3?
The term Web3 was coined by Ethereum co-founder, Gavin Wood, who is also the founder and lead developer of Parity Technologies and the creator of Polkadot and Kusama. Web3 essentially represents the next phase of the internet, consisting of decentralized applications (DApps) powered by blockchain technology.
Top Web3 Digital Assets
Polkadot
Described as a blockchain protocol that makes it possible to connect different blockchains into a unified network, Polkadot has been built with a vision to help users exercise control over their internet usage. Heterogeneous sharding, cross-chain composability, open governance, scalability, and upgradeability are some of the features built into Polkadot to give it notable advantages over legacy networks.
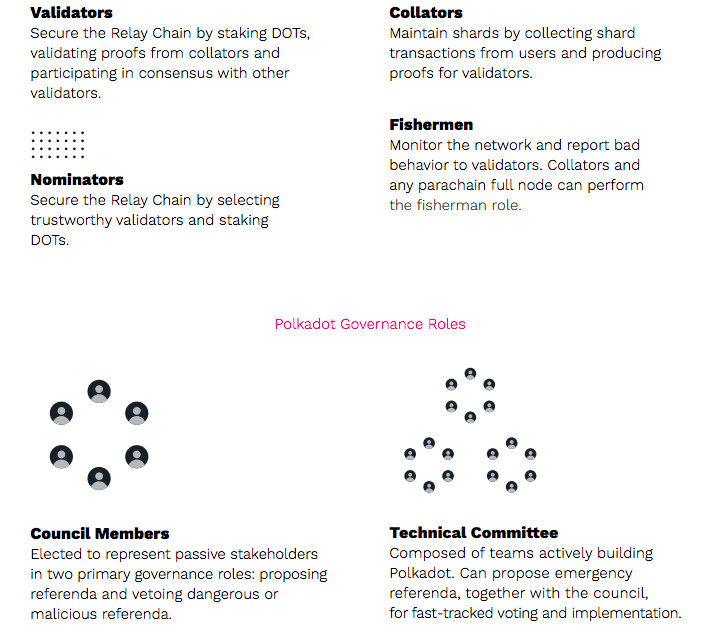
Some of Polkadot’s strengths include its capability to unite a network of heterogeneous blockchain shards that are called parachains that connect the to Polkadot Relay Chain which also secures the network and which is capable of connecting with external networks via bridges. Polkadot’s ecosystem is composed of several network participants.
The native token of the Polkadot platform is DOT which is used to carry out activity on the network. Some of the use cases of DOT tokens include ecosystem governance, staking, and bonding. DOT tokens can be traded on exchanges such as Kraken, Huobi, Bitfinex, Coinbase, KuCoin and others.
An early, unaudited and unrefined release of Polkadot called Kusama was created to test Polkadot’s network’s technology and economic incentives in a real-world environment. Kusama is recognised as the ideal platform for developers working on parachains to test out their ideas before deploying them to the Polkadot network. KSM tokens are the Kusama governance token.
Polkadot also includes Substrate which is a blockchain-building framework that is meant to make it easy for users to create custom blockchains that are optimized for unique use cases. Fully modular and flexible, Substrate makes it possible to mix and match ready-made components and build out core business logic.
Chainlink (LINK)
An enterprise-grade oracle infrastructure, Chainlink makes it possible for businesses or other organizations to securely connect their legacy systems to prominent blockchain networks. Chainlink enables entities to generate revenue from node operations.
Chainlink also makes it possible for enterprise systems to be able to read data from, and write data to, smart contracts. This consequently helps businesses digitize existing workflows securely while also addressing the issue of third-party risk. It enables access to real-world data and off-chain computation.
Chainlink through its network effectively helps secure billions of dollars within the decentralised finance (DeFi) ecosystem. It does so through connecting hybrid smart contracts with high-quality data and off-chain computation. Decentralized services such as data feeds, cross-chain interoperability, proof of reserve, keepers, and verifiable randomness function are all made possible by Chainlink.

In addition, Chainlink is now being used to automate claims processing and lower operating costs since it makes it possible for blockchain-based parametric insurance applications to get access to real-world data. In the fast-developing niche of NFTs, Chainlink is being leveraged to facilitate secure NFT minting, distribution, and trait assignment. It is also being used to bring secure entropy to blockchain games.
The $LINK token is the main means of transactional exchange on ChainLink. The token was developed from an ERC677 token and aligns with ERC-20 token standards. LINK tokens can be found on exchanges such as OKEx, FTX and Binance.
Filecoin (FIL)
Described as an open-source cloud storage marketplace, protocol, and incentive layer, Filecoin is effectively a peer-to-peer network and complementary protocol. Filecoin’s blockchain is based on proof-of-replication and proof-of-spacetime.
Filecoin’s mainnet first launched back in October, 2020 and the ecosystem has grown tremendously since. According to Filecoin, it now boasts 12 EiB of total network storage power, over 3,362 Filecoin storage providers and some 230+ organizations that are currently building on the network. Their developer community is a force to be reckoned with, with over 7,500+ project contributors on Github and over 10,000+ developers participating in Filecoin hackathons. More than 465 new projects entered the ecosystem in 2021 alone.

Essentially, Filecoin enables storage of files on the internet and provides data storage through a mechanism that incentivises users responsible for maintaining the network. What’s innovative is that pretty much anyone can participate in the storage and data retrieval open markets facilitated by Filecoin.
The way Filecoin’s ecosystem works is that users are able to pay others in order to store their files on storage miners. These miners are effectively computers that are responsible for file storage and proving proper file storage is in order. What’s great is that storage and storage price is not controlled by a single entity and users actually have the ability to choose between cost, redundancy, and speed through a simple process of simply selecting the miner whose storage offer is best suited to their storage requirements.