Futures Trading: How to Maximize Your Profits in the Crypto Market
Cryptocurrency futures trading has emerged as a powerful tool for traders looking to leverage their positions, hedge against risk, or capitalize on market volatility. Unlike spot trading, where you buy and sell the actual asset, futures trading allows you to speculate on the future price of a cryptocurrency without actually owning it. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about crypto futures trading – from its fundamentals to advanced strategies, and tips for managing risk.
What Are Crypto Futures?
Crypto futures are financial derivatives that represent a contract to buy or sell a specific cryptocurrency at a predetermined price at a specified future date. Traders do not own the underlying asset; instead, they enter into a contract that is settled at the expiration date.
Key Features of Crypto Futures:
- Leverage: Futures contracts often allow traders to use leverage, meaning they can control a larger position with a smaller amount of capital. This amplifies both potential profits and potential losses.
- Settlement: Contracts can be settled in two ways: physically, where the actual cryptocurrency is delivered, or cash-settled, where the difference between the contract price and the market price is exchanged in cash.
- Expiration Date: Futures contracts have a specific expiration date, after which the contract must be settled. Perpetual futures, however, do not have an expiration date and are renewed continuously.
- Margin Requirements: Traders must maintain a certain amount of capital (margin) in their accounts to open and maintain futures positions.
How Does Crypto Futures Trading Work?
Crypto futures trading is built on two primary concepts: long positions and short positions.
- Long Position: A trader buys a futures contract, betting that the price of the underlying cryptocurrency will increase in the future. If the price rises, the trader profits.
- Short Position: A trader sells a futures contract, betting that the price of the underlying cryptocurrency will decrease in the future. If the price falls, the trader profits.
Traders use these positions in various combinations to hedge existing holdings, speculate on market movements, or leverage their exposure.
Types of Crypto Futures Contracts
-
Perpetual Futures Contracts: These are futures contracts that do not have an expiration date. They are among the most popular types of contracts in the crypto market. To keep the contract price aligned with the spot market price, exchanges use a funding rate mechanism. Traders who are “long” pay a funding fee to those who are “short” and vice versa, depending on the market conditions.
-
Quarterly or Monthly Futures Contracts: These contracts have a set expiration date, such as the last Friday of the month or quarter. The prices of these contracts converge to the spot market price at expiration. They are often used by institutional traders for arbitrage or to hedge against market risks.
-
Inverse Futures Contracts: In these contracts, the margin and payout are denominated in the cryptocurrency being traded (e.g., Bitcoin). This is the opposite of a linear futures contract, where the margin is denominated in USD or a stablecoin.
Key Exchanges for Crypto Futures Trading
- Binance Futures: Offers a wide range of perpetual and quarterly futures contracts with leverage up to 125x. It also supports isolated and cross-margin modes, catering to both beginners and advanced traders.
- Bybit: Focuses on perpetual contracts with leverage up to 100x. Known for its advanced trading tools and competitive fee structure.
- BitMEX: One of the pioneers in the crypto futures market, offering perpetual contracts with up to 100x leverage. It is known for its deep liquidity and strong focus on security.
- OKX: Offers a wide range of futures products, including perpetual and dated contracts, with leverage up to 100x.
Key Concepts in Crypto Futures Trading
Leverage and Margin
Leverage allows traders to amplify their exposure to the market by using borrowed capital. For example, with 10x leverage, a trader can open a $10,000 position with just $1,000 in their account. While leverage can magnify profits, it also increases the risk of liquidation.
Margin refers to the collateral required to open and maintain a leveraged position. This is typically categorized into two types:
Initial Margin: The amount of capital required to open a position.
Maintenance Margin: The minimum amount of equity needed to keep a position open. If your equity falls below this level, your position is at risk of liquidation.
Cross Margin vs. Isolated Margin
Cross Margin: Shares the available margin balance across all open positions, reducing the risk of liquidation by using all available funds as collateral. However, this can lead to a complete loss of all funds if the market moves against your position.
Isolated Margin: Restricts the amount of margin allocated to a specific position. Only the margin allocated to that position is at risk, while the rest of the account balance remains protected.
Funding Rate and Premium Index
- Funding Rate: A periodic payment made between traders based on the difference between the perpetual contract price and the spot price. If the funding rate is positive, long position holders pay short position holders and vice versa. This mechanism keeps the futures contract price aligned with the spot price.
- Premium Index: Represents the difference between the futures price and the spot price, reflecting the market sentiment. A positive premium indicates bullish sentiment, while a negative premium suggests bearish sentiment.
Strategies for Crypto Futures Trading

Directional Trading Strategies
- Long Strategy: Used when a trader expects the price of a cryptocurrency to rise. The trader opens a long position to profit from the upward movement. This strategy is straightforward but carries significant risk if the market moves in the opposite direction.
- Short Strategy: Applied when a trader anticipates a decline in the cryptocurrency price. By opening a short position, the trader profits from the downward movement. This strategy is ideal in bearish markets or when expecting a price correction.
Hedging Strategies
- Portfolio Hedging: Traders with a large spot position in a cryptocurrency might open a short futures position to hedge against potential losses. This strategy protects against downside risk without selling the underlying asset.
- Arbitrage: Involves exploiting price differences between different exchanges or markets. A trader might buy a cryptocurrency on one exchange and simultaneously sell a futures contract on another exchange where the price is higher, profiting from the difference.
Spread Trading Strategies
- Calendar Spread: Involves simultaneously buying and selling futures contracts with different expiration dates. The trader profits from the convergence or divergence of the prices of the two contracts.
- Inter-Exchange Spread: Takes advantage of price differences between the same contract traded on different exchanges. For example, a trader might buy a Bitcoin futures contract on Binance and sell it on Bybit if there is a price discrepancy.
Advanced Strategies
- Basis Trading: Involves buying the spot asset and selling the equivalent amount in futures to capture the premium between the spot and futures price. This strategy is typically employed when futures are trading at a significant premium to the spot price.
- Grid Trading: A strategy that automates buying and selling at predetermined intervals, creating a grid of orders at incremental price levels. This is particularly useful in a ranging or sideways market.

Risk Management in Crypto Futures Trading
Position Sizing: Proper position sizing is essential in managing risk, particularly when trading with leverage. Traders should never risk more than a small percentage of their account on a single trade.
Stop-Loss Orders: Placing stop-loss orders is critical in protecting against unexpected market moves. This order automatically closes a position when the market reaches a predetermined price, limiting potential losses.
Diversification: Avoid putting all your funds into a single trade or asset. Diversification across multiple positions and assets can mitigate the risk of significant losses.
Understanding Liquidation Risks: Leverage can amplify losses, leading to liquidation if the margin requirement is not met. Traders must understand their margin requirements and monitor their positions closely to avoid forced liquidations.
Using a Trading Journal: Keeping a detailed trading journal helps track performance, refine strategies, and identify mistakes, enabling continuous improvement.
Psychological Aspects of Futures Trading
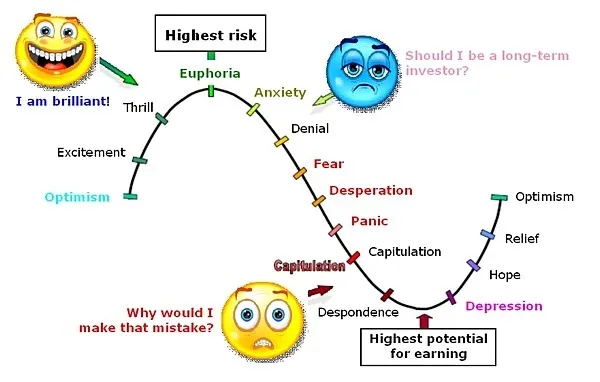 Discipline and Patience: Futures trading requires a high level of discipline and patience. Over-leveraging, revenge trading, and ignoring risk management principles can lead to significant losses.
Discipline and Patience: Futures trading requires a high level of discipline and patience. Over-leveraging, revenge trading, and ignoring risk management principles can lead to significant losses.
Emotional Control: Traders must control emotions like fear and greed, which can cloud judgment and lead to poor decision-making. Adopting a systematic trading approach and sticking to a pre-defined plan can help mitigate emotional bias.
Continuous Learning: The crypto market is highly volatile and constantly evolving. Traders must continuously learn and adapt to new market conditions, tools, and strategies.
Choosing the Right Exchange for Crypto Futures Trading
Selecting the right exchange is crucial for successful futures trading. Key factors to consider include:
Security: Look for exchanges with strong security measures, such as cold storage, two-factor authentication, and regular audits.
Liquidity: High liquidity ensures tighter spreads and better execution prices, reducing slippage and enhancing trading efficiency.
Leverage Options: Choose an exchange that offers the desired leverage levels but be cautious with high leverage.
Final Thoughts: Is Crypto Futures Trading for You?
Crypto futures trading is not for everyone, but for those willing to educate themselves, manage risk effectively, and develop disciplined strategies, it can be highly rewarding. It offers flexibility, high-profit potential, and the opportunity to trade in both directions of the market. However, the inherent risks, especially with leverage, mean that traders should approach this market with caution, patience, and a well-structured plan.
By understanding the tools at your disposal, applying intelligent strategies, and practicing sound risk management, you can significantly improve your odds of success in the volatile world of crypto futures trading.