Notional Finance (NOTE) Review

Introducing Fixed Rates to the Crypto Ecosystem
A decentralized protocol that is deployed to the Ethereum blockchain, Notional Finance makes it possible for anyone to lend or borrow crypto assets at a fixed-rate of interest at any time, from anywhere in the world. Decentralised application (DApp) developers can also utilize the protocol to develop apps.
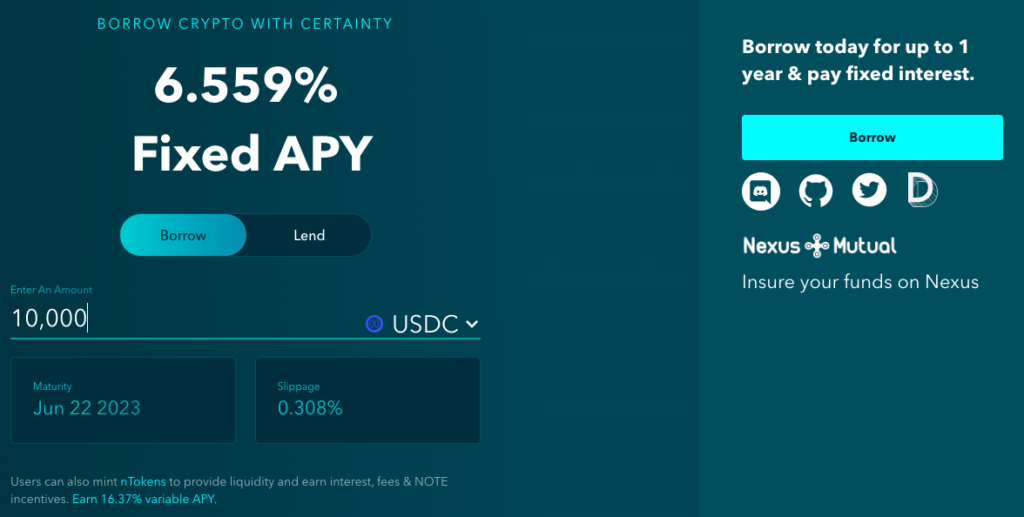
Unlike many other protocols that tend to only either serve lenders at fixed rates, or offer unstable, variable interest rates, Notional aims to serve both sides of the fixed-rate borrowing and lending market.
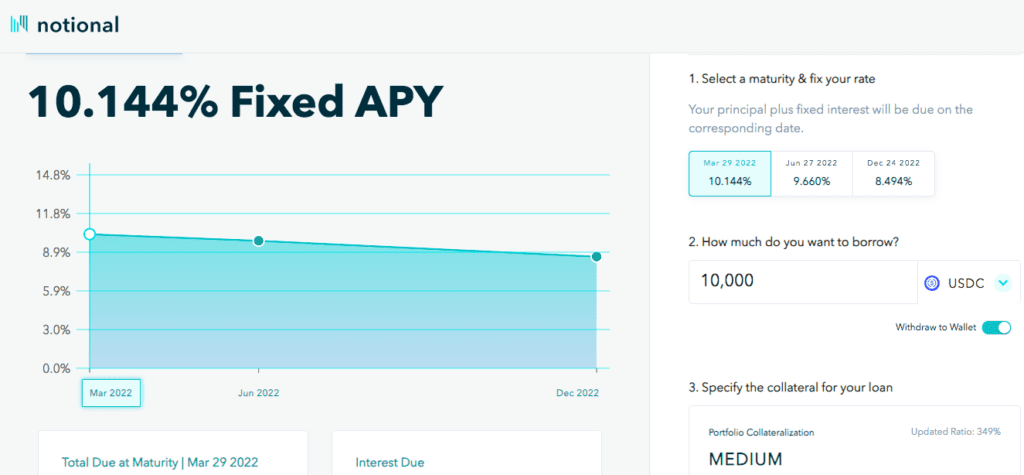
An automated market maker is used to update the interest rate based on a user’s trade size. The current market’s supply and demand determines the rate and that varies with each individual loan. Nevertheless, once executed, a user’s rate will be fixed for the duration of the loan.

Notional Finance’s protocol facilitates fixed-rate, fixed-term crypto asset lending and borrowing through a novel financial instrument called fCash. fCash are essentially described as transferable tokens that at a specific point in the future, represent a claim on a positive or negative cash flow.
The liquidity pools on Notional Finance are capitalized by liquidity providers who contribute cTokens which are effectively interest-bearing assets that are native to the Compound protocol. These cTokens are used within Notional in order to provide liquidity providers with better returns. Liquidity providers, acting as counterparties to the active lenders and borrowers on the protocol, essentially contribute cTokens and fCash to liquidity pools and in exchange they earn fees each time a lender or borrower makes a trade between cTokens and fCash.
The process of providing liquidity is quite straightforward on Notional Finance. A liquidity provider has to specify the amount of cash they want to supply and nominate the specific liquidity pool they wish to supply the liquidity to. From there, they are able to mint a pair of fCash tokens. In order to receive liquidity tokens as rewards, the liquidity provider can then deposit their cTokens and the positive fCash into the liquidity pool. The liquidity tokens in this case actually represent their proportional claim on the cTokens and fCash tokens that are available in the specific liquidity pool the provision is being assigned to. The liquidity provider’s obligation is offset by the positive fCash their liquidity tokens entitle them to. Furthermore, a liquidity provider is at any time able to redeem their liquidity tokens for the underlying assets.
Notional ensures borrowers pay back their debt at maturity thereby guaranteeing that lenders earn the expected returns. Borrowers are required to have high-quality assets such as ETH or wBTC locked-in as collateral. The amount of collateral typically varied based on the risk level. DAI for instance ETH requires 150% collateralization while the stablecoin DAI only requires 120% collateralization.
Both lenders and borrowers are given fixed interest rates on Notional. These stay fixed over the course of the maturity which is not the case on many platforms – those that at times may offer stable rates but only at a premium – and often alter the rates when market conditions shift.
NOTE ($NOTE token) is the governance token of Notional protocol. It is an ERC-20 token that holders can use for proposals, votes, and implementing changes to Notional system parameters and smart contracts. NOTE is currently traded on Balancer (v2) and DODO (ERC-20).
To purchase NOTE tokens, it’s simpler to use decentralized non-custodial platforms via MetaMask for example.
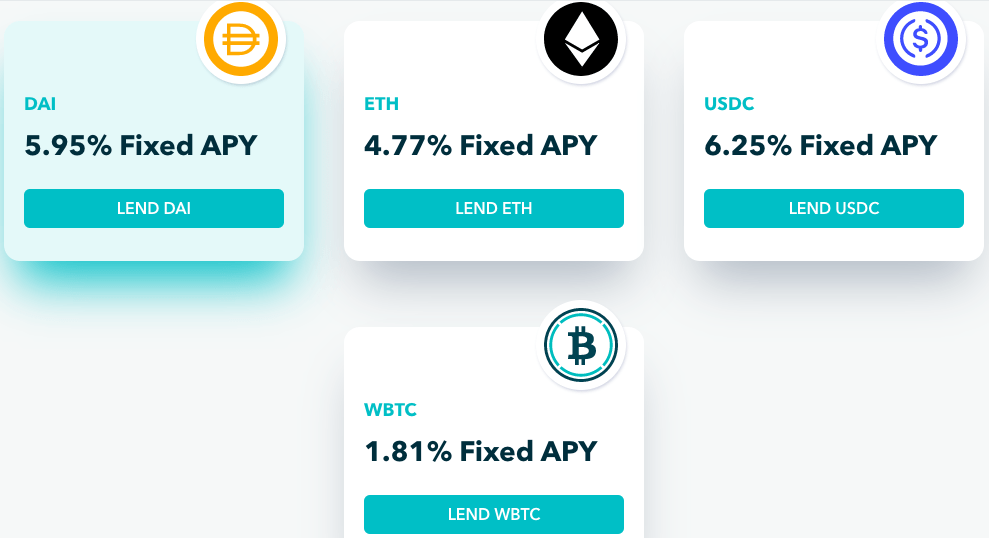
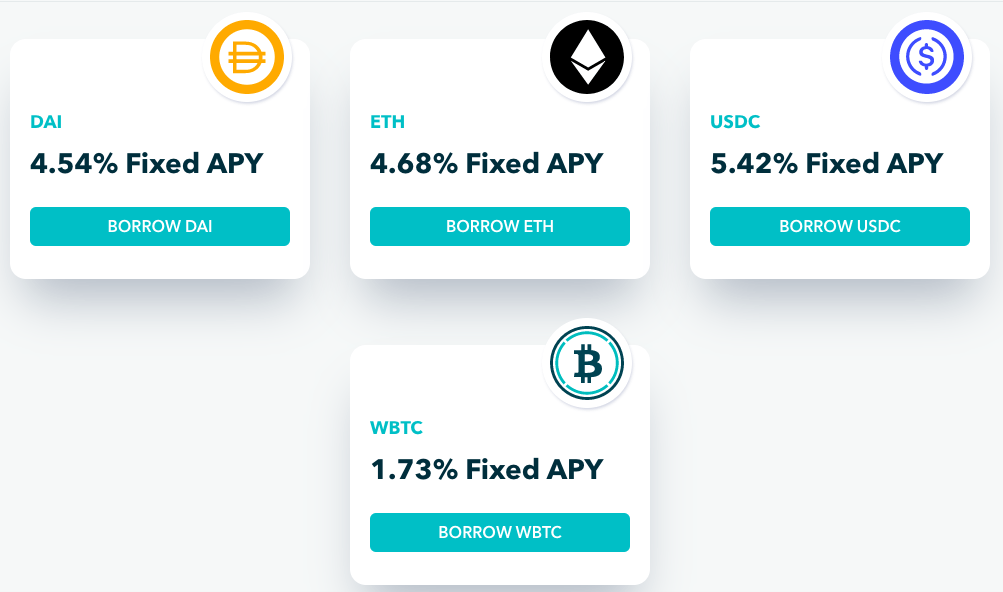
Currently Notional allows users to borrow or lend DAI & USDC which are stablecoins for a term of up to one year. Users can also borrow ETH and wBTC from Notional’s on-chain liquidity pools for a period of up to 6 months.
Notional launched its V2 upgrade which doesn’t require liquidity providers to roll their debts to new maturities since that’s now done in an automated fashion through the use of nTokens which are essentially the main avenue through which users are able to provide liquidity to Notional. According to Notional, nTokens are simply ERC20 assets that can be redeemed for a share of Notional’s total liquidity in a particular currency across all active maturities.
According to Notional, users can mint nTokens by depositing cTokens into the nToken account which then distributes the user’s liquidity into the underlying liquidity pools for that currency based on a set of governance parameters called deposit shares. Deposit shares essentially instructs the nToken account on how much of a user’s total liquidity ought to be deposited into each individual market. Deposit shares also make it possible for Notional governors to direct liquidity to the maturities where the end-user demand for borrowing and lending is greater.
The nToken account also holds the resultant liquidity tokens which represent the nToken account’s claim on the user’s deposited liquidity.
Notional has some notable blockchain companies backing them including Coinbase Ventures and Pantera, among others.

Notional v3
Notional V3 has introduced the prime money market, which is a new lending and borrowing market that offers variable rates, making the protocol more accessible and powerful for DeFi users. The core value proposition of Notional as a fixed rate lending protocol is also strengthened by this addition. The prime money market is integrated directly with Notional’s fixed rate markets to enhance yields and user experience for fixed rate users and LPs, while also introducing new variable-rate functionality.
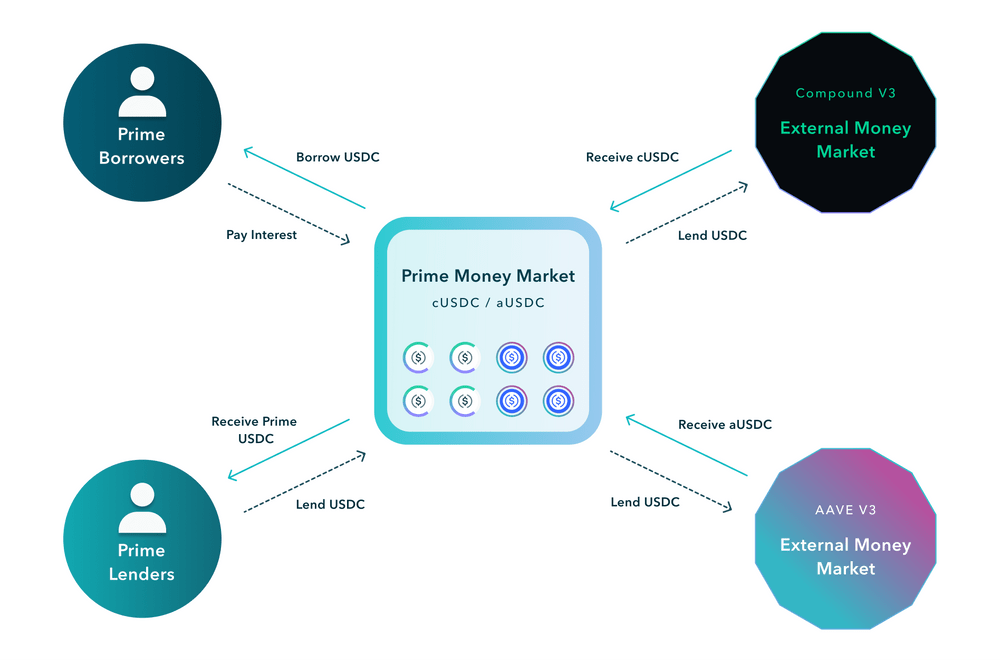
The impact of the prime money market on Notional users includes high yields for variable-rate lenders and LPs, better UX for fixed rate borrowers, leveraged interest rate trading, and the ability to enter into a leveraged vault on a variable-rate, open term basis.
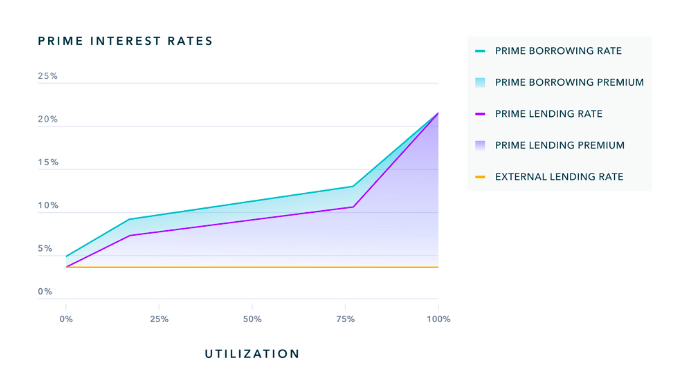
Additionally, the prime money market will drive the growth of the protocol and improve its utility and UX for all users. By increasing organic returns for LPs, the protocol will also sustainably decrease NOTE incentive emissions.

Notional V3 also includes new features and improvements such as multi-currency leveraged vaults that allow users to borrow in two or more currencies simultaneously, an upgraded AMM that increases LP efficiency by around three times and decreases slippage for fixed rate lenders and borrowers, and increased integration flexibility that allows governance to allocate underlying tokens to other money markets without disrupting protocol operations.
Staking $NOTE Tokens
Upon staking your NOTE, it will be converted into 80/20 NOTE/ETH Balancer LP tokens. You can stake with 100% NOTE, proportional shares of NOTE and ETH, or 100% ETH if you want to purchase NOTE and stake simultaneously.
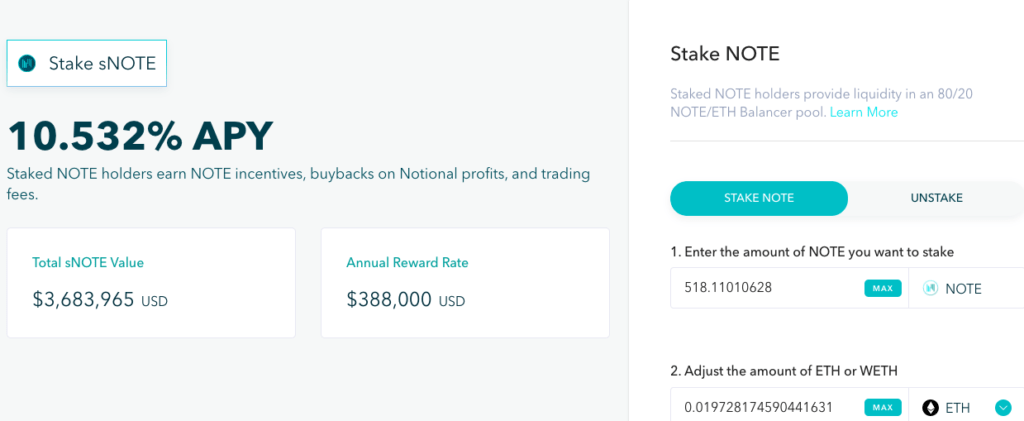
You can check the current APY being offered when you stake and you can choose how much you want to stake.
You can then pay off the gas fees.
Once you have staked your NOTE, your sNOTE will become redeemable for the Balancer LP tokens. The number of Balancer LP tokens that sNOTE holders can redeem will increase as they earn rewards.
By staking NOTE, users can earn additional 80/20 NOTE/ETH Balancer LP tokens. These rewards are funded by protocol revenues and an additional incentive of 30,000 NOTE per week.
However, NOTE stakers are exposed to impermanent loss from the Balancer pool. In a collateral shortfall event, up to 50% of sNOTE assets can be used to recapitalize the Notional system.
Unstaking NOTE requires a mandatory 15-day cooldown period. After initiating the cooldown period, users can unstake their NOTE during the three-day redemption window (Day 16-18) following the cooldown period (Day 1-15). If unstaking is not completed within the redemption window, users must restart the 15-day cooldown period.
Why Notional Finance matters
Having fixed interest rates provides borrowers and lenders with certainty and fixed-rate financing is crucial to the attainment of healthy financial markets. The majority of debt in developed economies such as the US is typically issued using fixed rates of interest. What Notional is attempting to do is perhaps akin to ushering in perceived stability into the decentralised finance (DeFi) space.