Ramses Decentralized Exchange Review

What is Ramses Exchange?
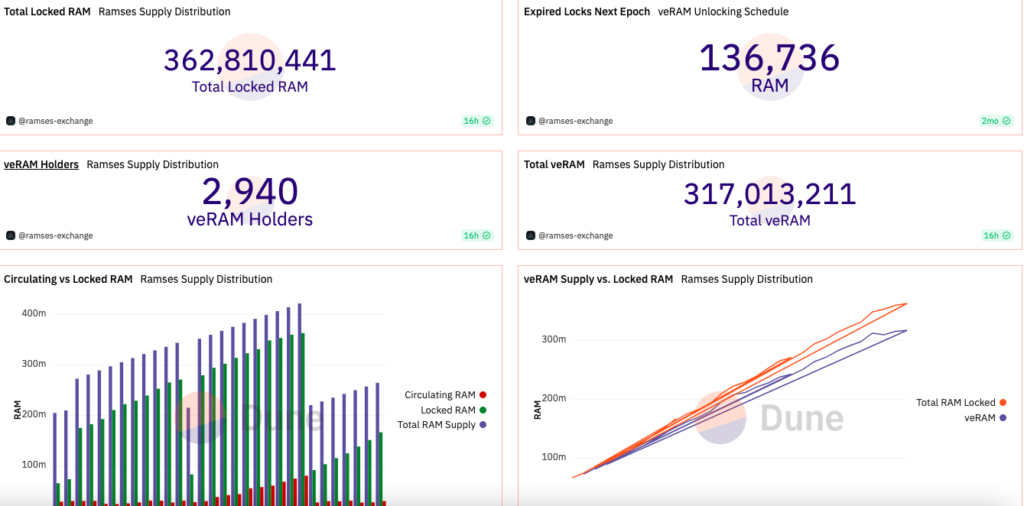
RAMSES is an innovative ve(3,3) DEX that stands out in the decentralized exchange landscape. It’s established on the Arbitrum blockchain, a Layer 2 solution that’s EVM compatible with Ethereum. Arbitrum enhances transaction speeds with its optimistic rollup, boasting around 40,000 TPS. This results in swift and cost-effective transactions. The design of RAMSES intertwines Andre Cronje’s vision of Solidly, introducing a fresh take on the voting-escrow model. With its progressive decay embedded, the RAM model is built for sustainability, rewarding long-standing supporters and aligning stakeholders via fee generation.
RAMSES’ Three Pillars:
-
Community: RAMSES is committed to nourishing a lively community. A testimony to this is its initiative to offer veNFTs to leading protocols on Arbitrum. Such veNFTs grant protocols the ability to maneuver their positions aligning with their platform’s interests.
-
Decentralization: The DEX pursues maximum decentralization while maintaining functionality. A dedicated council of trusted members oversees emergency decision-making, safeguarding platform integrity and security.
-
Functionality: Adopting the most advanced features from existing DEXs, RAMSES aims for a user-centric experience.
Trading on RAMSES
To use Ramses, simply connect your web3 wallet.
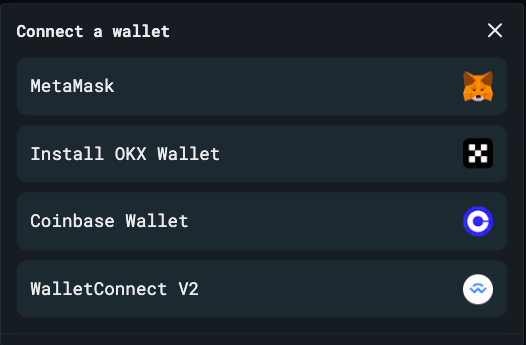
Make sure you’re using the Arbitrum network.

Swaps on Ramses
Users can effortlessly exchange tokens. The slippage and trade rate are influenced by the total value secured in liquidity pairs and prevailing arbitrage activities.
- Types of Liquidity Pools:
- Volatile (UniV2-Style): Here, tokens are paired with equal dollar-value weights, facilitated by a volatile swap curve.
- Correlated (Andre-Style): Featuring a stable swap curve, it promises minimal slippage, revering Andre’s pioneering stable swap approach.
Fee Structure
- Default Fees:
- Volatile Pair (vrAMM): 0.2%
- Correlated Pair (crAMM): 0.01%
- Native pairs (vAMM – RAM/wETH): Initially set at 0.5%
Note: The RAMSES multisig can adjust fees, keeping them competitive and appealing for veRAM holders.
Voting Mechanisms
The essence of veRAM NFT is to direct emissions to LP token pairs through voting. The epoch sees a proportional distribution of emissions based on the vote percentage.
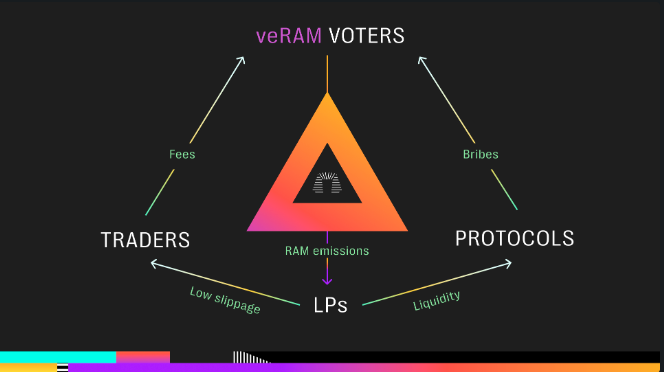
Strategic Bribing
Types of Bribes:
-
Vote Bribes: Users and protocols can propose bribes to sway voters, guiding emission allocations.
-
Gauge Bribes: Directly offered to LP stakers, these stimulate liquidity growth in specified token pairs.
Vesting (veNFT Management)
Managing veRAM (veNFT) positions is essential. Users and protocols can navigate the vesting page to tweak their ve lock durations, merge or set up a new veRAM position.
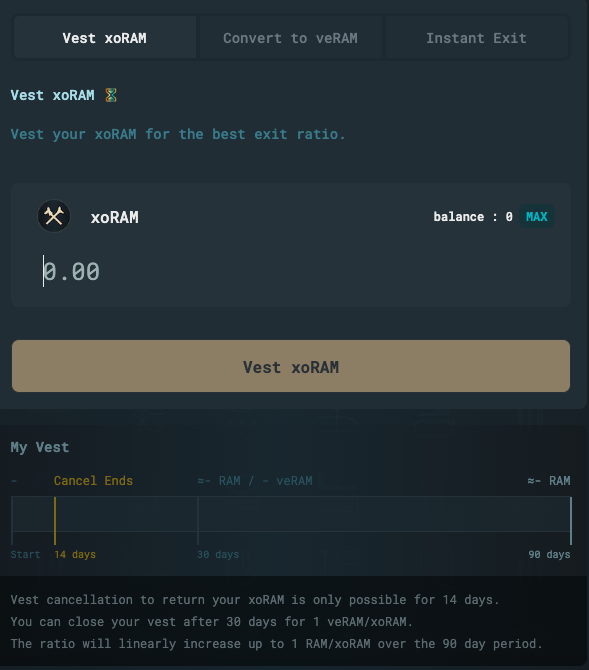
LP Staking
While all fees are directed to veRAM holders, staking gauges reward LP token providers with promising APRs. The allocated votes for a pair determine the emitted RAM in the subsequent epoch.
Distinct Features of RAMSES
- A unique approach to liquidity pairing with incentive multipliers and liquidity concentration.
- Revenue generation is directed majorly to veRAM voters.
- Locked tokens receive swap fees from the pools they vote for, motivating active participation.
- 100% of fees are channeled to veRAM holders, with LPs earning RAM through token emissions influenced by staking gauges.
$RAM Token
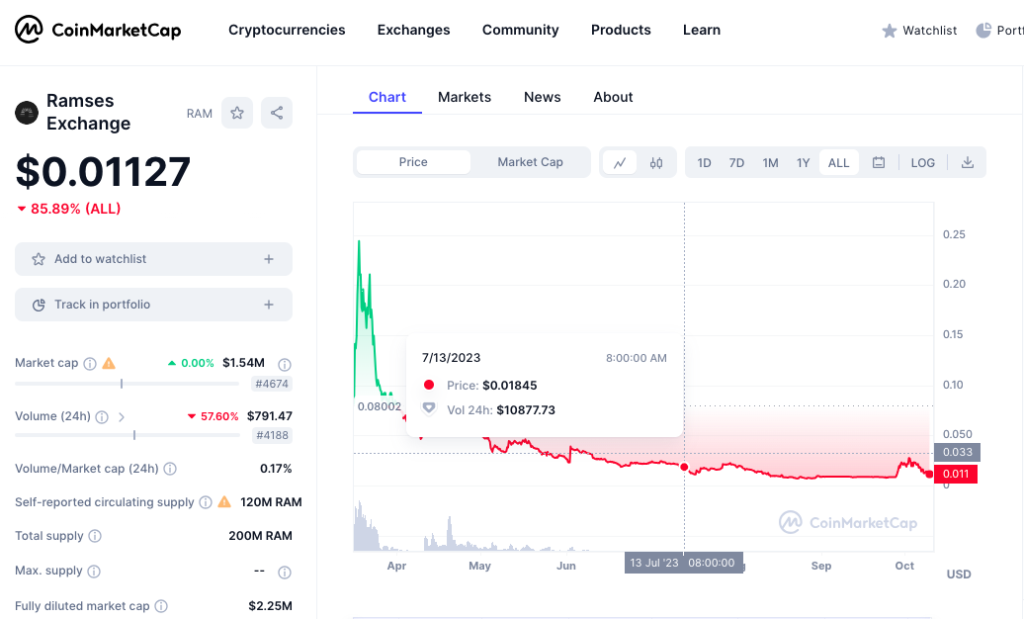
RAMSES’ native token, $RAM, when locked into the platform, bestows users with veRAM. This allows voting on token emission directions and liquidity allocation. Employing the ERC-721 protocol, veNFTs represent unique asset positions. It’s noteworthy that $RAM can be accessed on exchanges, including Poloniex, Uniswap(v3), Balancer, OpenOcean, etc.
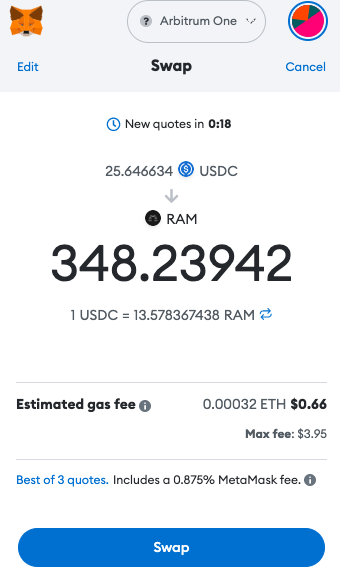
Alternatively you can just use a web3 wallet to purchase RAM from different decentralized exchanges.