Centrifuge – On-chain Infrastructure for Real-world Asset Tokenization
What is Centrifuge?
Centrifuge serves as the underlying infrastructure that enables the decentralized financing of real-world assets directly on-chain. This creates a fully transparent market where borrowers and lenders can interact without the need for unnecessary intermediaries.
Asset pools within the Centrifuge ecosystem are entirely collateralized, ensuring that liquidity providers have legal recourse. Furthermore, the protocol is not limited to a specific asset class, accommodating a wide range of assets, including mortgages, invoices, microlending, and consumer finance. Essentially, Centrifuge is an on-chain ecosystem for structured credit where institutional investors earn yield backed by tokenized RWAs.
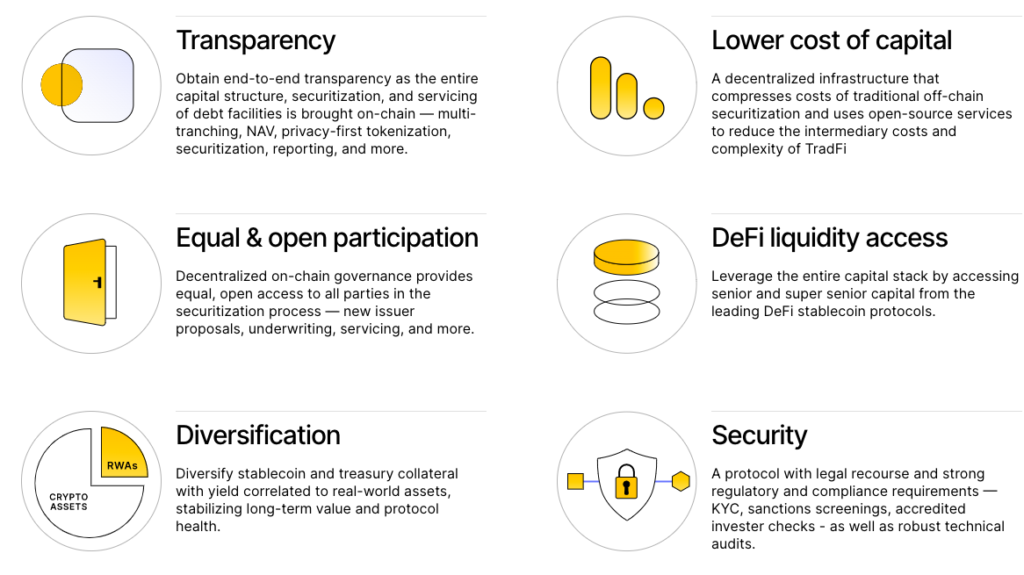
The ultimate goal of the Centrifuge protocol is to reduce borrowing costs for businesses worldwide, while simultaneously providing DeFi users with a stable, collateralized yield source that is uncorrelated to the volatile cryptocurrency markets. By incorporating the entire structured credit market on-chain – including securitization, tokenization, privacy, governance, and liquidity integrations – Centrifuge is paving the way for a more transparent, cost-effective, and boundless financial system. This innovative approach has the potential to revolutionize the way we interact with financial markets and reshape the future of decentralized finance.
How Centrifuge Protocol Works
The Centrifuge Protocol comes equipped with a comprehensive suite of features that facilitate the financing of real-world assets on a blockchain. These features encompass everything from tokenization and securitization to liquidity integrations, all of which are built upon each other and governed in a transparent manner by the token holders.
At the heart of the protocol is the Centrifuge Chain, a layer-1 blockchain specifically designed for real-world assets. This blockchain operates as a parachain within the larger Polkadot ecosystem. The Centrifuge Chain’s native token, CFG, functions as an on-chain governance mechanism. This mechanism enables CFG holders to actively participate in managing the evolution and development of the Centrifuge Protocol, thus ensuring a democratic and decentralized approach to decision-making.

Real-world assets within the Centrifuge ecosystem are tokenized as Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) to provide an on-chain representation. These tokens are associated with detailed off-chain data that accurately reflect the nature and value of the asset. The tokenized assets are then pooled together and securitized by the issuer, creating a secure and trustworthy ecosystem.
Moreover, connectors are available to bridge the Centrifuge Protocol to other blockchains, enhancing interoperability and flexibility. The protocol also boasts of integrations with notable DeFi protocols like Maker and Aave, among others, ensuring a robust and interconnected ecosystem that’s primed for growth and innovation.
Financing real-world assets necessitates a concrete legal structure that aligns with the practical realities of such assets. To this end, each pool within the Centrifuge ecosystem is carefully designed to reflect both the protocol structure and the real-world relationships between various parties involved. These designs draw upon templates that are based on legal structures which have been widely utilized for asset-backed securitizations for several decades.
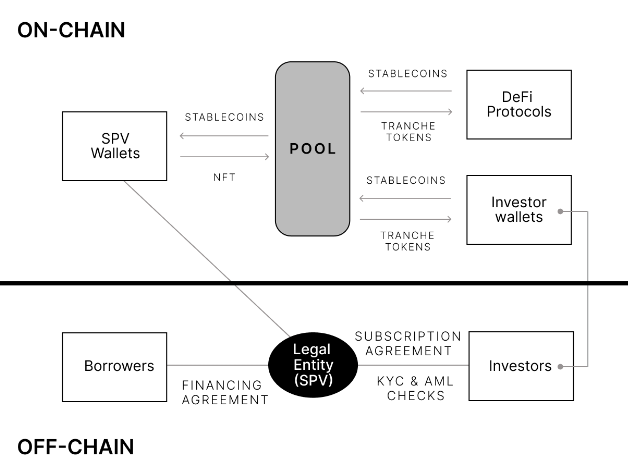
Each pool is associated with a legal entity known as a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV). The SPV serves to keep the asset originator’s business distinct from the financing activity related to the pool. Moreover, it ensures that the assets within the pool are protected from bankruptcy risks associated with the asset originator. An Operating Agreement dictates the operations of the SPV, providing a framework for its function and governance.
To securitize assets, the legal ownership of these assets is transferred from the asset originator to the SPV. In the event of an asset default, the pool issuer is responsible for the recovery of the capital. The method for recovery varies depending on the asset class. For instance, an issuer may aim to purchase and replace any non-performing loan with a performing loan, and then handle collections independently on their own balance sheet. Any proceeds from the recovery process are converted into stablecoins and distributed to token holders as the borrower repays the loan either partially or in full.
How to Use Centrifuge
To get started on the app, go to https://tinlake.centrifuge.io/
You’ll need to connect your web3 wallet e.g. MetaMask.

Once you’re connected to the platform, you can then proceed to be onboarded as an investor by going through the KYC process. Once that is completed, you’ll be able to participate in the real world asset token offerings.
In terms of investor onboarding for a pool, the issuer must ensure that Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations are adhered to. This also includes accredited investor verification and tax form submission. Centrifuge collaborates with a third-party e-KYC provider to offer an integrated onboarding system as a service to issuers. These service providers verify investor KYC information and confirm the accredited investor status for US-based investors. Once verified, investors can then enter into a Subscription Agreement with the issuer.
The platform has undergone several audits to ensure reliability.

To acquire CFG governance tokens, simply swap from ETH for example to the wrapped version of CFG i.e. wCFG.


CFG Tokenomics
The Centrifuge Token Model is the driving force behind the Centrifuge platform, offering the necessary framework for the platform to operate independently of centralized third parties and amplify its utility. This model is built around the native token of Centrifuge, known as CFG.
Transaction fees on the Centrifuge Chain are paid in CFG, and the token is also used for staking value. An on-chain governance mechanism allows CFG holders to vote on potential chain upgrades, effectively giving them the power to influence the development of Centrifuge. Coupled with CFG rewards, this governance mechanism fosters a community of users who are committed to promoting the long-term growth and sustainability of Centrifuge.
Any modifications to the Centrifuge protocol or the CFG token model must be proposed through governance proposals and approved by CFG token holders.
CFG Utility
CFG tokens serve a specific purpose within the Centrifuge ecosystem. They are used for standard network operations like ensuring chain security and paying transaction fees, as well as for on-chain governance. Moreover, they support unique Centrifuge-specific functions that enable the financing of Real-World Assets on-chain. Increased utility and participation in the network contribute to strengthening the network.
Utility Value
As Centrifuge’s utility increases, the value captured by CFG will also rise, reflecting the growing benefits offered to the network’s users. This value is primarily accrued through the use of CFG for transaction fees and its crucial role in the network’s governance.
The CFG Token Model ensures the security of the Centrifuge Chain and encourages a decentralized network of agents to perform essential network functions by offering CFG Network Rewards.
Token Supply
Minting Mechanisms
In the short term, the token supply of CFG will increase as it is minted for securing the chain and incentivizing a distributed network of agents with CFG Network Rewards. The annual mint rate depends on the different rewards distributed that year, which may include: rewards for chain security, rewards for liquidity providers, and a block reward for the on-chain treasury.
Once the network’s inherent utility attracts enough users (and consequently, sufficient transaction fees for the on-chain treasury), the mint rates can be adjusted downwards through a vote by CFG holders.
Burning Mechanisms
A predetermined portion of the transaction fees will be burned at a rate set by on-chain governance. Over time, this burning mechanism will serve to regulate the overall supply of the token.
CFG Token Distribution
Initial Distribution
The initial CFG Generation Event was carried out by the Centrifuge Network Foundation. This event led to the creation of 400,000,000 CFG, which was distributed among the Foundation, initial contributors, including the core team, investors, and validators. Post-genesis, additional tokens have been minted as rewards for securing the chain and incentivizing adoption. This broad token distribution is fundamental to Centrifuge’s decentralization.

Mechanisms of Token Distribution
The Centrifuge Chain employs rewards, paid out in CFG, to motivate the early involvement of network participants and finance the ongoing development of Centrifuge. In addition to fees, these rewards stimulate entities to perform essential network functions. By encouraging early participation, the network stands to benefit by establishing a dependable and distributed network of agents from the outset. Further, a burning mechanism is in place to ensure a consistent token supply over time.
Token Lockups
Token lockups play a significant role in aligning the incentives of token holders with the long-term growth of the Centrifuge ecosystem.
Most CFG tokens are subject to long-term lockups upon distribution. For instance, core team members face 48-month lockups upon joining, with a 12-month cliff. Typically, CFG sales are also under long-term lockups. Rewards might be subject to lockups as well.
Governance
CFG tokens serve standard network functions like chain security and also allow holders to participate in technical governance. Token holders can vote on proposals to upgrade the chain runtime code, proportional to their stake in the protocol. This on-chain voting mechanism enables CFG holders to participate in governance. Runtime upgrade proposals are voted on by token holders, and approved proposals are implemented directly on-chain.
Transaction Fees
Users on the Centrifuge Chain pay transaction fees in CFG. These fees are directed to the on-chain treasury. A portion of these fees can also be allocated to network agents who carry out crucial functions, such as nodes running the chain. CFG token holder governance can set a rate at which a percentage of fees is burned.
To learn more about real world asset tokenization, check out Tokenized Trillions – The Digitization of Real-World Assets Using Blockchain Technology.